Faster processor communications to better understand fluid turbulences
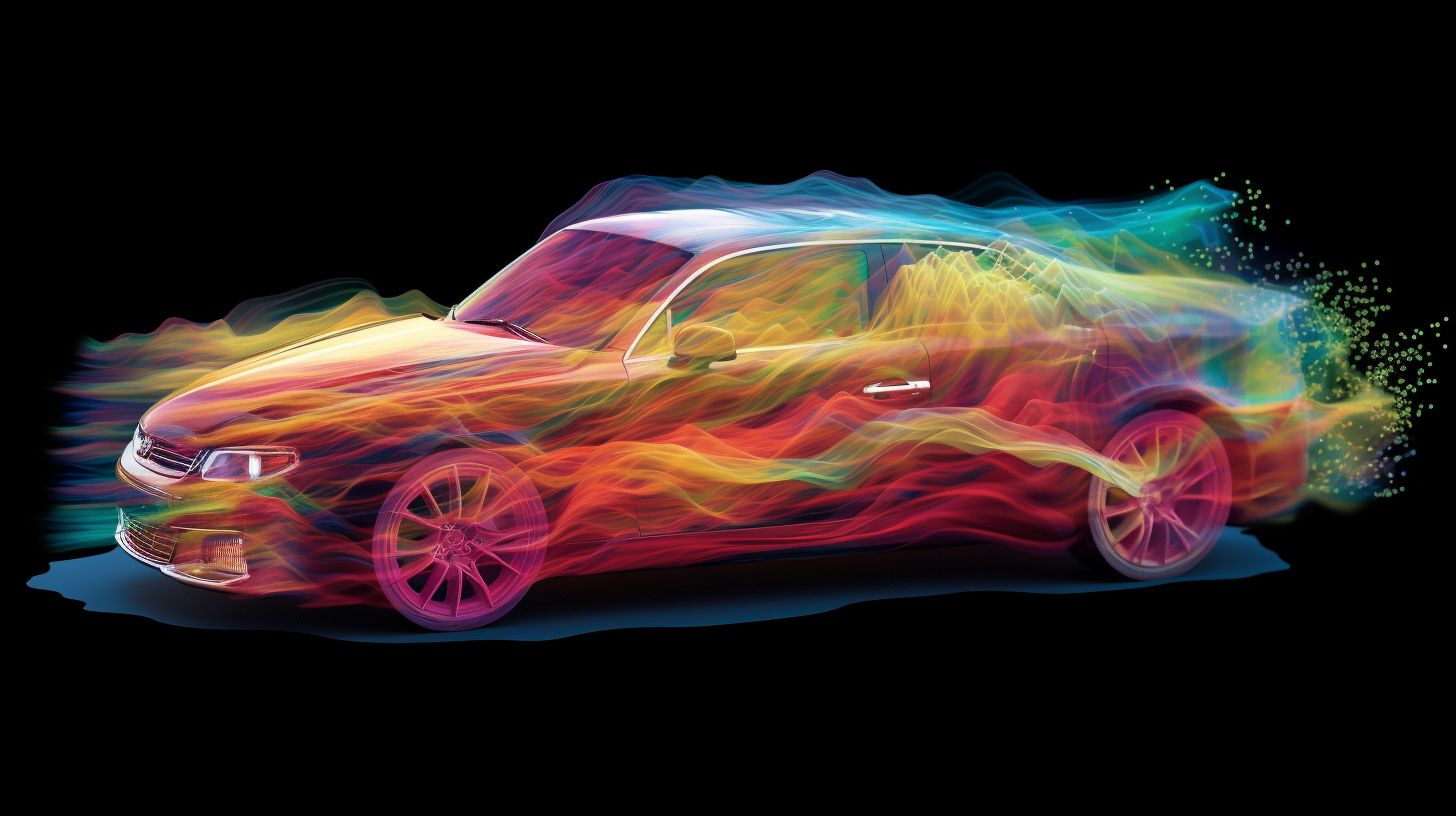

Whether it's designing more efficient wind turbines ⚡, faster cars ?️, or more fuel-efficient aircraft ✈️, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is an essential tool for researchers. To obtain accurate results, it is sometimes necessary to describe complex structures with great precision, which can require very substantial computing resources; hence, the use of supercomputers. However, implementing CFD methods efficiently on HPC infrastructures is not straightforward, as a lot of communication is inherently required between the different processing units of the supercomputer.
In this user story, Pierre Balty, from Ph. Chatelain’s lab, explains where this limitation comes from and how they work on efficient parallelisation methods, pushing back the limits of what is possible in CFD.